NEUROSURGERY
Laser microsurgery was used successfully on the brain for the first time in 1969 by Steller et al. (Stellar, Polanyi et al. 1970) who used a CO₂ source with continuous emission for the ablation of a recurrent glioma.
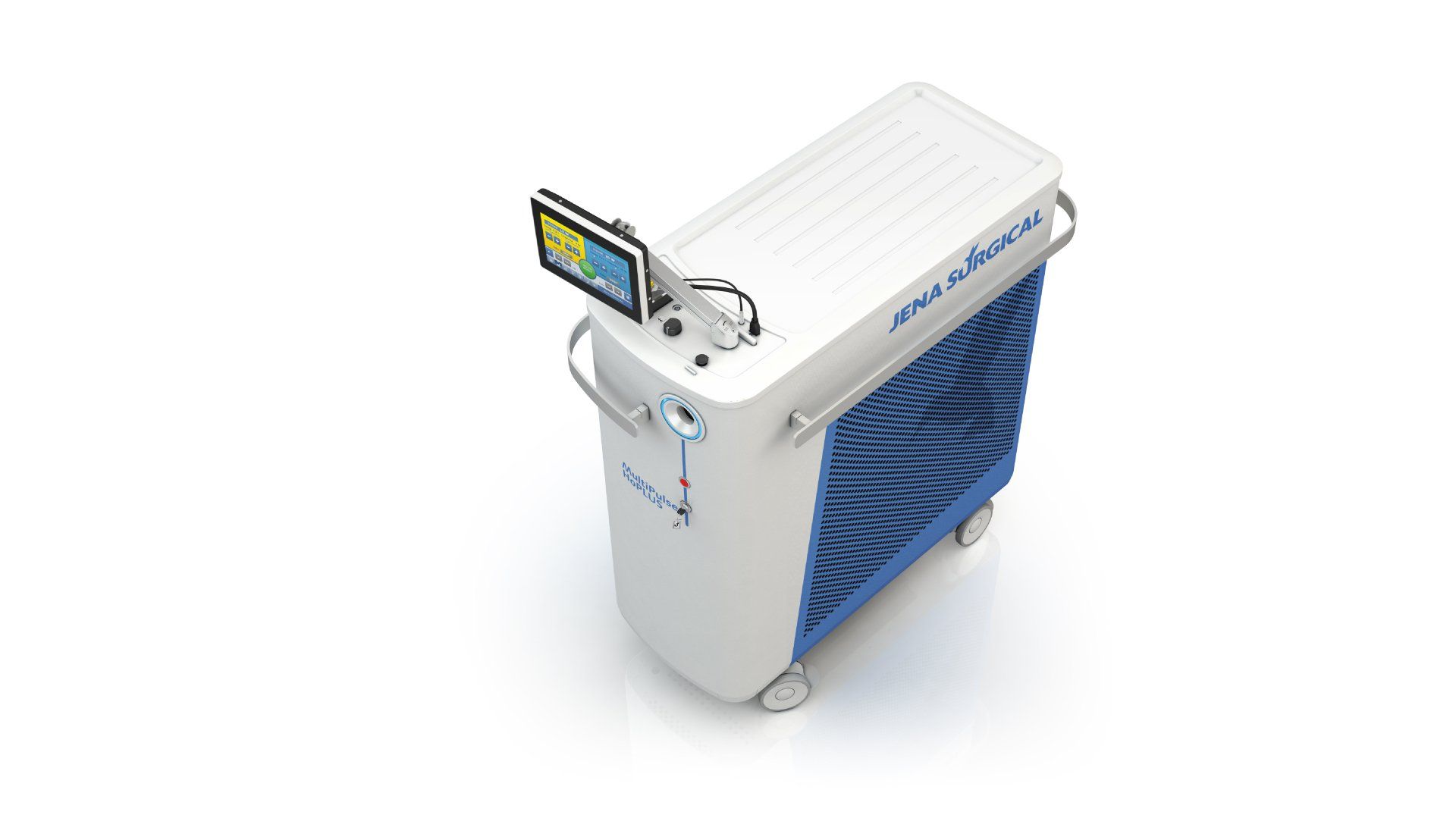
The CO₂ laser technology enables selective removal of the tumor area while minimizing damage to the healthy brain tissue. Due to this fact, it is widely used in neurosurgery, especially for the removal of localized tumors in difficult areas to reach.
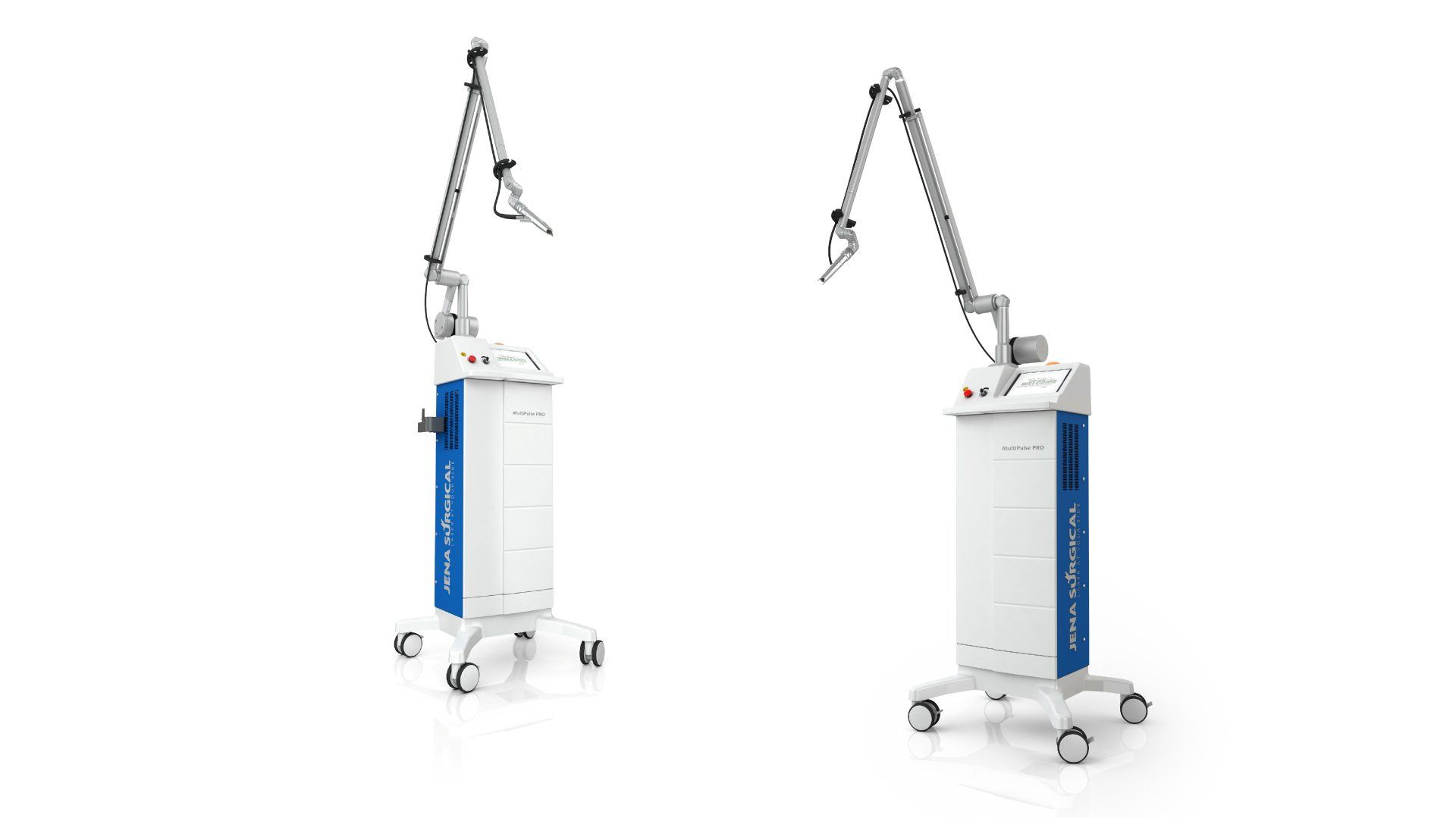
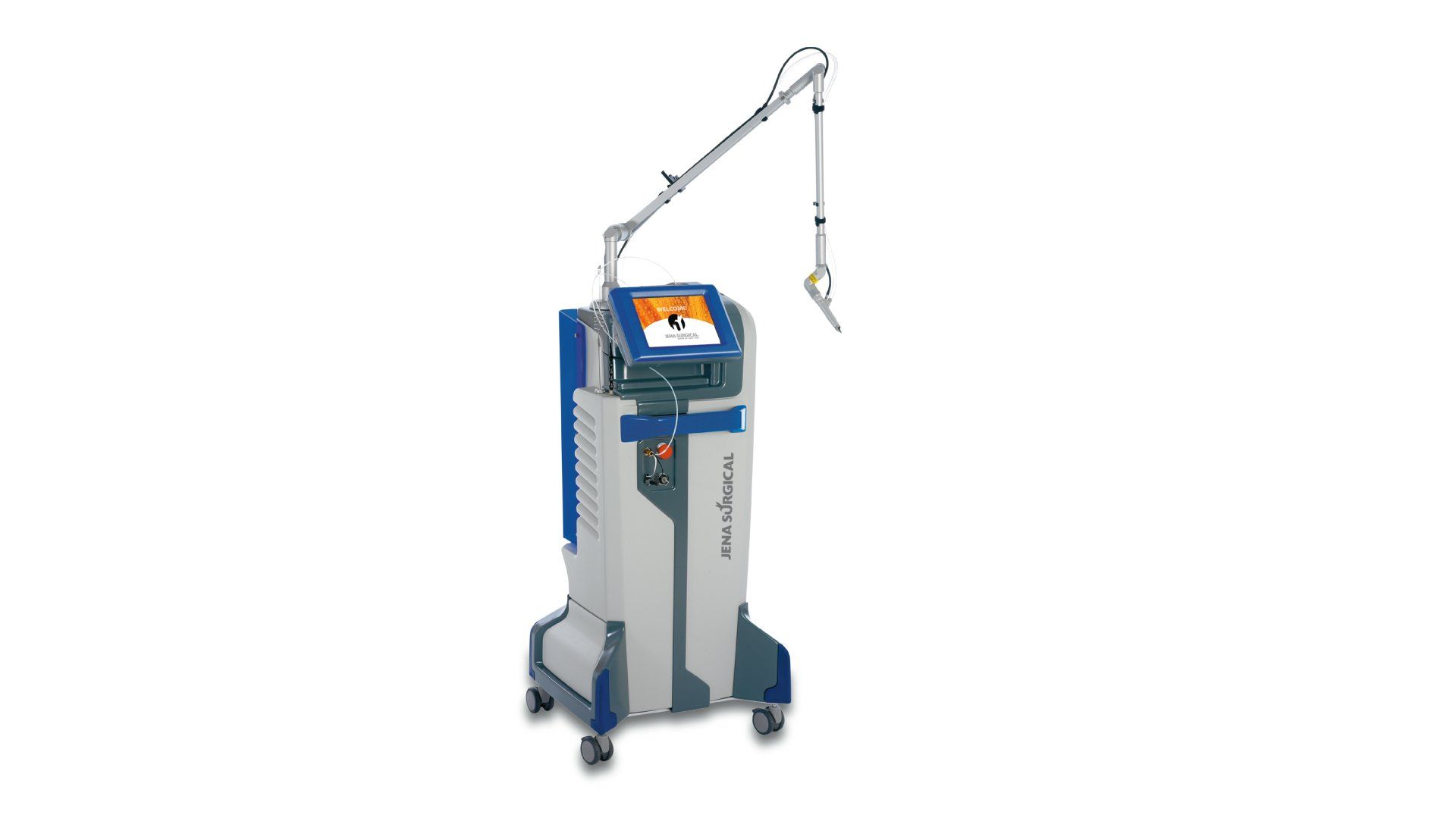
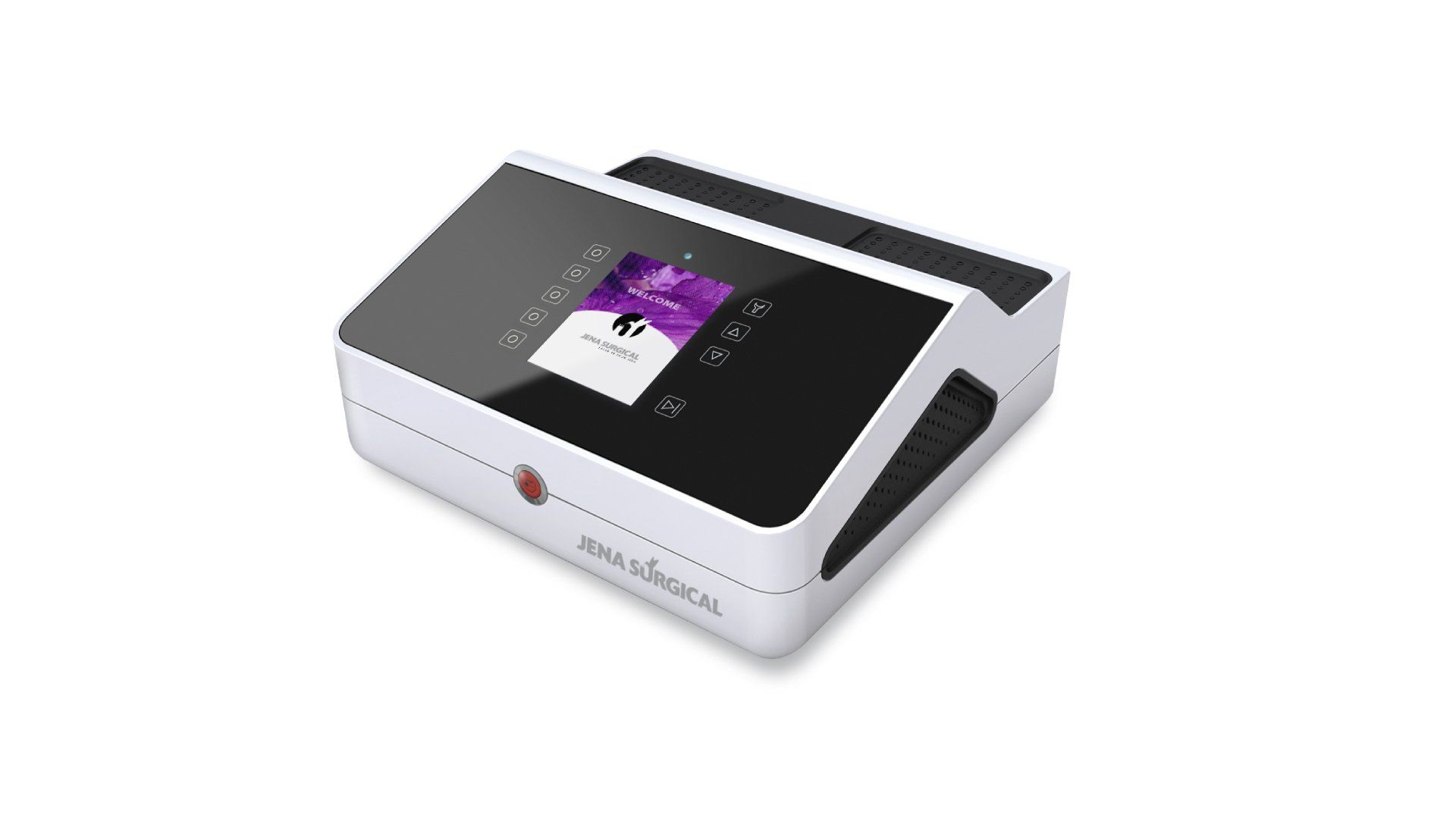
Using the SmartXide² high-precision accessories (i.e EasySpot Hybrid micromanipulator and the HiScan Surgical scanning system), the neurologist can perform delicate microscope-assisted brain surgery.
Optimized topographical precision, appropriate energy dosage and proper emission mode guarantee minimally invasive and quick photoablation of the tissue.
How CO₂ laser microsurgery can guarantee the best performance in the operating room for neurosurgery:
The use of the laser in neurosurgery presents remarkable advantages:
• It enables operation in narrow surgical fields.
• It enables tumor removal while minimizing lateral thermal damage to healthy tissue.
• It minimizes damages due to shrinkage of brain tissue.
• It reduces bleeding in the surgical field due to its excellent hemostatic effect.
• It improves asepsis thanks to cutting with sterilization and, in case of the CO₂ laser, to the no-touch dissection.
• It reduces the time needed for surgery.